Multi-modal Learning
Multimodal Learning for improving Non-English Classification tasks
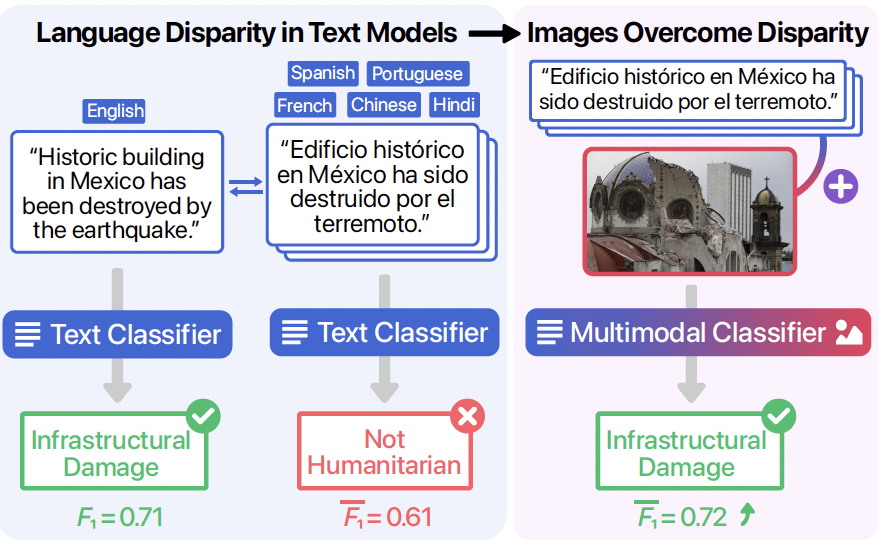
We use multimodal (image + text) learning to overcome the language disparity that exists between English and non-English languages. The figure illustrates an example of a social media post that is correctly classified in English but misclassified in Spanish. Including the corresponding image leads to correct classification in Spanish as well as other non-English languages
This project was done as part of the course CS 7643 Deep Learning at Georgia Tech.
We investigated different multi-modal deep learning architectures with a focus on bridging performance gap in classification in English language vs non-English (Hindi in our study) lanugage tasks. The term multi-modal here means that we used both textual and image based inputs (modes) while training our classification model.
Our aim was to:
- Conduct a comparative analysis of different text and image networks, to understand which architectures work best.
- Understand how much images can improve the discrepancy in performance between English and non-English text classification models.
We used CrisisMMD dataset for training and testing our models.
You can read our full report in the github repository, but to be brief we:
- Trained a ResNet-18, VGG network, and Inception-V3 to compare different deep learning architectures and to compute image embeddings.
- Fine-Tuned two pre-trained BERT models, DistilmBERT (distilbert-base-multilingual-cased on HuggingFace) to classify the English text and HindiBERT for Hindi (Doiron 2020).
- Finally we implement a multimodal or fusion classifier that combines the embeddings of both text and image data to perform classification based on the joint modeling of both input modalities.